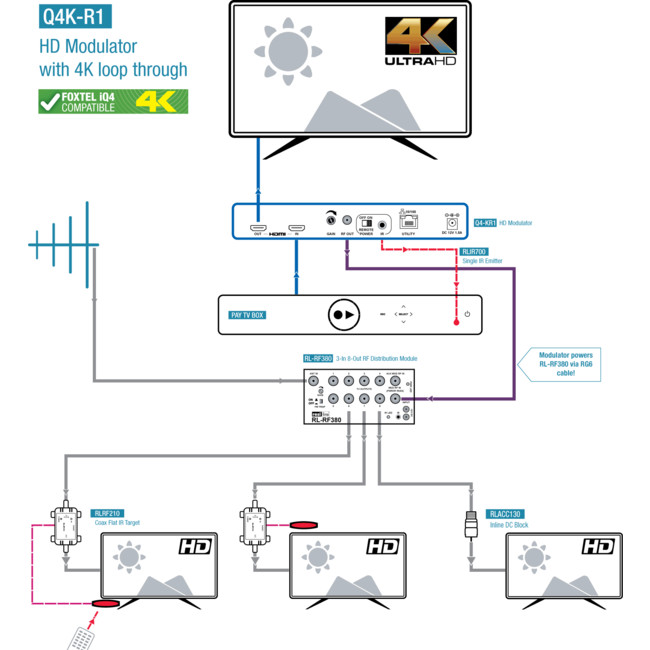
Description
Zycast Q4K-R1 Single Input HDMI HD Modulator with 4K Pass Through
Introducing the new Zycast Q4K-R1 HDMI modulator, the replacement for the industry’s most popular modulator –the HD1603– Now with 4K loop-out! The Q4KR1 not only will accept a 4K signal but allows you to retain that 4K signal on your main TV while modulating a 1080p signal to the rest of your house!
We have been testing the new Q4K-R1 for months now, while the Q4K-R1 is not the first 4K modulator on the market, it’s the first stable 4K modulator. Like the HD1603, the Zycast Q4KR1 HDMI Modulator supports Resi-linx IR targets and emitters. Resi-linx are the market leader in both IR and modulation and the only brand to have Foxtel approved product in both fields.
The Zycast Q4KR1 HDMI Modulator has full menu via LCD display, improved MER resulting in higher quality picture and is configurable for New Zealand. Q4K-R1 allows you to distribute any HD source around your home/business installation over coax cable and control with ease.
Features
- Most cost effective fully featured 4K HD modulator on the market
- Single input digital modulator encoding HD video and stereo audio signals to MPEG-4 only(H.264) DVB-T COFDM TV channels
- Compatible input resolutions 576i/720P/1080i& 1080P/UHD/4K for high definition picture quality (ensure TV tuner is MPEG4/H.264 and 4K HDCP2.2 compatible)
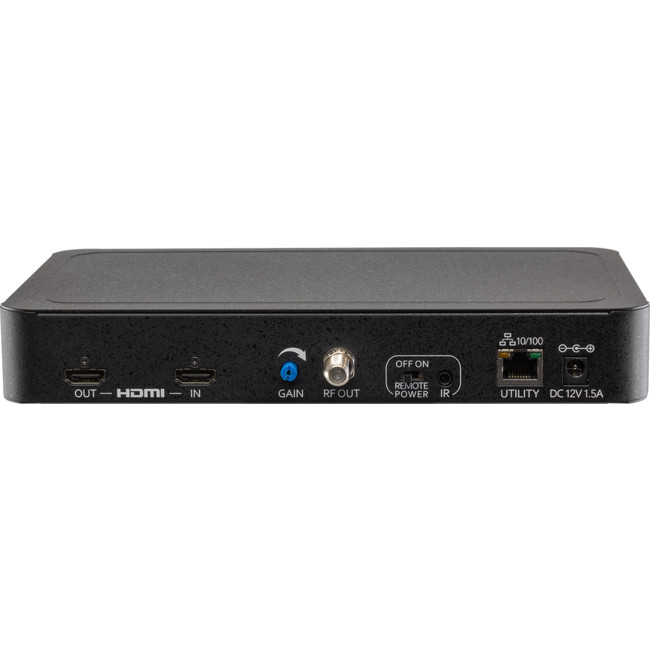
- HDMI input-with HDMI loop through for local connectivity
- IR return path- compatible with resi-linx RL-RF380(video hub) and Rl-RF210(IR target)
- Superior error rate (MER 39)
- Full function front LCD display with menu driven configuration
- New Zealand channel plan selectable
- 2K/8K carriers
- Adjustment of settings available via WEB GUI
- Remote management with a PC
- Adjustable VHF/UHF output (6-69)
- 85dB launch with adjustable attenuation
- Compact design
- Silent operation-NO FAN NOISE!
For the Foxtel approved Zycast KT-FX1, please follow this link.
What’s the difference between MPEG2 and MPEG4?
DVB-T (Digital Video Broadcasting – Terrestrial) is a standard for transmitting digital television signals over terrestrial (over-the-air) broadcast networks. MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 are video compression standards used in DVB-T to encode the video content.
- DVB-T MPEG-2: DVB-T MPEG-2 refers to the use of the MPEG-2 video compression standard within the DVB-T system. MPEG-2 is an older compression standard that was widely used for digital television broadcasting before the introduction of MPEG-4. It offers moderate compression efficiency, which means it requires more bandwidth to transmit video compared to MPEG-4 for the same quality. MPEG-2 provides good video quality, especially for standard definition (SD) content, and it is still compatible with many older television sets and receivers.
- DVB-T MPEG-4: DVB-T MPEG-4, on the other hand, uses the more advanced MPEG-4 video compression standard. MPEG-4 offers better compression efficiency, allowing broadcasters to transmit higher quality video using less bandwidth compared to MPEG-2. This is especially beneficial for high-definition (HD) and other bandwidth-intensive content. MPEG-4 can deliver superior video quality with the same amount of data or equivalent video quality with less data compared to MPEG-2. However, MPEG-4 requires more processing power for encoding and decoding, which means older television sets or receivers may not support MPEG-4 without a compatible decoder.
In summary, the main difference between DVB-T MPEG-2 and DVB-T MPEG-4 lies in the video compression standard used. MPEG-2 is an older standard with moderate compression efficiency but good compatibility with older devices, while MPEG-4 is a more advanced standard offering better compression efficiency for higher quality video but requiring more processing power and compatibility considerations.
How can I tell if my TV is MPEG2 or MPEG4?
Early digital TVs sold in Australia had MPEG2 DVB-T Tuners. Later models have progressed to MPEG4. Any MPEG4 TV will work with MPEG2 signals. However MPEG2 TVs will not work with MPEG4 signals including those from MPEG4 modulators.
It is often difficult to see from the TV’s specifications if the hardware is MPEG2 or MPEG4. The easiest way is to test the TV with a normal broadcast antenna signal. New HD Channels such as Channel 70 (7HD) or Channel 31 (SBS Viceland HD) are broadcast in MPEG4. If your TV produces a black picture or an error message such as FORMAT NOT SUPPORTED, then this TV is MPEG2 only.
To correct a MPEG2 only TV, a new DVBT Set Top Box can be used to tune the RF signal and convert it to a HDMI input on the TV.